Influenced by Europe & Asia
According to legend, Rome was founded on 21 April 753 BC by the twin brothers Romulus and Remus, who were descended from the Trojan prince Aeneas.
The city of Rome actually grew from settlements around a ford on the river Tiber, probably in the 8th century BC. The Roman Republic was established around 509 BC, when the last of the seven kings of Rome, Tarquin the Proud, was deposed. In 27 BC, Octavian took the name Augustus and this date is usually taken as the beginning of the Roman Empire. The fall of the Western Roman Empire is generally said to be in 476 AD although the Eastern Empire continued until the fall of Constantinople in 1453.
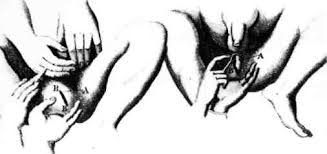
 Much of Roman medicine is derived from the Greeks and the famous work of Aulus Cornelius Celsus, "De Medicina", is based on Alexandrian medicine. Celsus described perineal lithotomy for bladder stone (above right) in great detail. Roman medical instruments have been found in Pompeii, including an “S”-shaped silver catheter (below right).
Much of Roman medicine is derived from the Greeks and the famous work of Aulus Cornelius Celsus, "De Medicina", is based on Alexandrian medicine. Celsus described perineal lithotomy for bladder stone (above right) in great detail. Roman medical instruments have been found in Pompeii, including an “S”-shaped silver catheter (below right).
Roman Doctors
Many of the famous Roman doctors were Greeks but, of course, the geographical extent of the Roman Empire meant that Roman citizens came from all over Europe and Asia.
Galen of Pergamon
 Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus (c129 AD - c 216 AD, pictured right) was born in Pergamon, now Bergama, in Turkey. He was a famous physician, surgeon and philosopher. He became the doctor to many prominent members of Roman society and personal physician to several emperors.
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus (c129 AD - c 216 AD, pictured right) was born in Pergamon, now Bergama, in Turkey. He was a famous physician, surgeon and philosopher. He became the doctor to many prominent members of Roman society and personal physician to several emperors.
Galen's theories dominated and influenced medical science for more than 1,300 years and medical students continued to study Galen's writings until well into the 19th century. His ideas were eventually disproved by modern research e.g. much of his anatomical work was disproved by Andreas Vesalius (1543), and his theory of circulation by William Harvey (1628).
 Celsus
Celsus
Aulus Cornelius Celsus (c 25 BC - c 50 AD, pictured right) was a Roman encyclopaedist, rather than a doctor, but he is famous for his well known medical book, "De Medicina". It was a primary source on diet, pharmacy and surgery for centuries and was one of the best sources of medical knowledge in the Roman world.
In urology, he is known for his description of the Celsian method of cutting for bladder stone.
Rufus of Ephesus
Rufus of Ephesus (late 1st century AD) was a Greek physician and author who wrote the very first textbook of urology, “On Diseases of the Bladder and Kidneys”.
Soranus
Soranus (1st / 2nd century AD, pictured right) was a Greek physician from Ephesus.
He practiced in Alexandria and Rome during the reigns of Trajan and Hadrian (98 AD - 138 AD) and is most famous for his four-volume treatise on gynaecology.
Dioscorides
 Pedanius Dioscorides (c 40 AD - 90 AD, pictured right), was a Greek botanist, pharmacologist and physician who practiced in Rome at the time of Nero.
Pedanius Dioscorides (c 40 AD - 90 AD, pictured right), was a Greek botanist, pharmacologist and physician who practiced in Rome at the time of Nero.
He became a famous Roman Army doctor.
Dioscorides wrote a five volume encyclopedia, "De Materia Medica", listing over 600 herbal cures, which was used extensively by doctors for 1,500 years.
← Back to Time Corridor